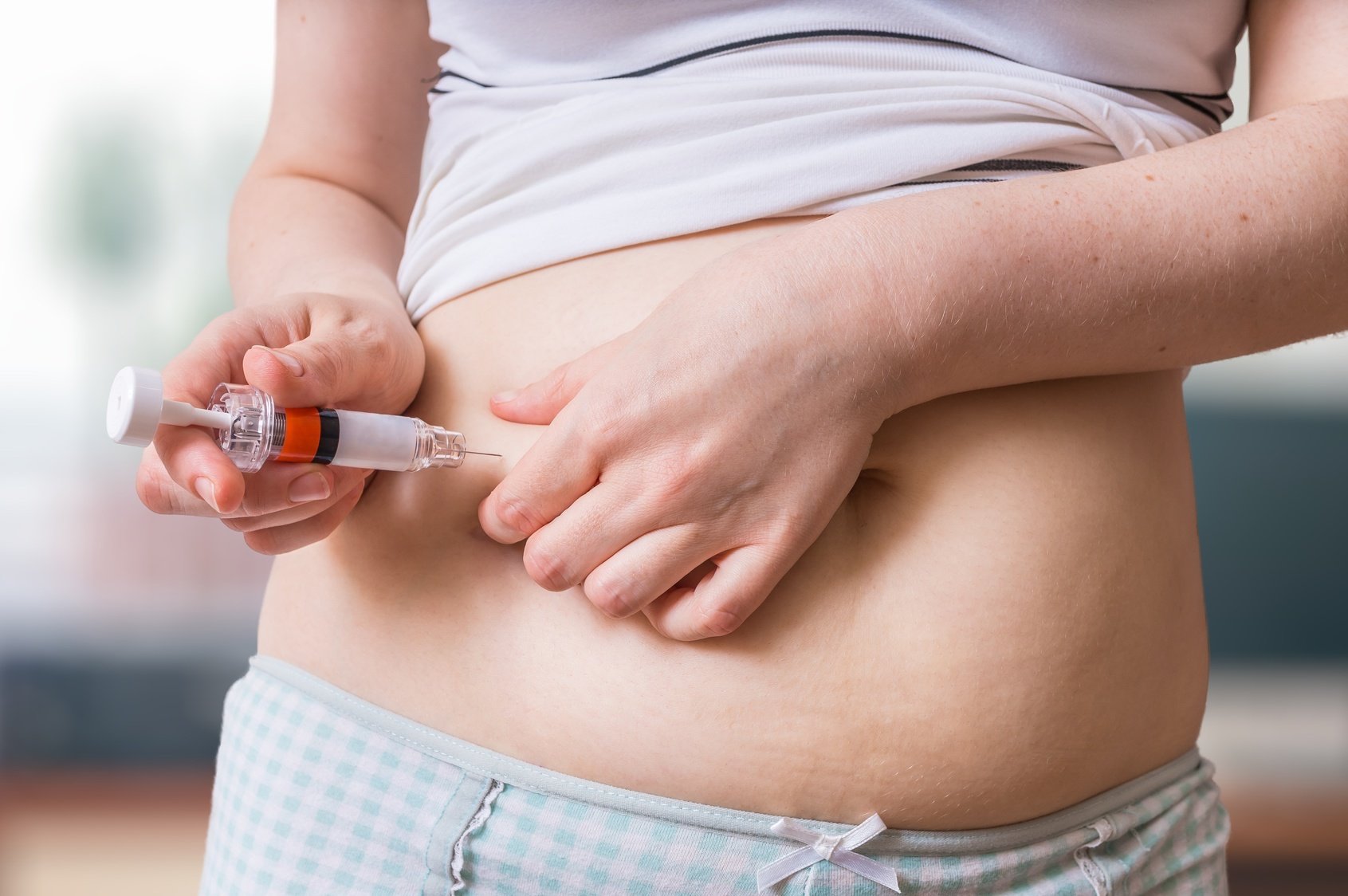
Patients undergoing fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), and ovulation induction are typically prescribed injectable fertility medication that must be self-administered at home at various intervals between office visits. These medications serve a variety of purposes including stimulating a woman’s reproductive system to produce eggs, preventing premature release of the eggs, and triggering ovulation at the desired time.
Though it may seem intimidating at first, most patients become comfortable with the injection process with a little time and practice. Some patients find it helpful to enlist the assistance of their partner or a close family member.
Most fertility medication injections are obtained at a specialty pharmacy rather than a typical drugstore. Specialty pharmacies have physical locations, but many operate online. In some cases, insurance companies will specify a preferred specialty pharmacy that offers the best coverage and rates for their subscribers.
Additionally, there are often coupons and discounts available for fertility injections. Patients may also wish to explore self-pay options depending on what is covered in their insurance plan.

Click each medication to view a step-by-step instructional video for administering the injection. If you are unsure about any of the steps involved in the process, please do not hesitate to call our office with questions.
The documents linked contain visual timelines related to different types of IVF cycles. These can help patients more clearly understand the timing of office visits, injections, monitoring, egg retrievals, and embryo transfers. They are in PDF format and may be downloaded or printed for easy reference.
Specific instructions for subcutaneous (under the skin) or intramuscular (into the muscle) fertility treatment injections vary by medication. But there are some general tips and best practices.
Send Us A Message
90 Plain Street,
Providence, RI 02903
Copyright © 2026 Care New England Health System